Browser Object Model
class: center, middle .title[ Front-end training # Window, BOM, RegExp ] --- # Window Object It represents the browser's window. All global JavaScript objects, functions, and variables automatically become members of the window object. Global variables are properties of the window object. Global functions are methods of the window object. 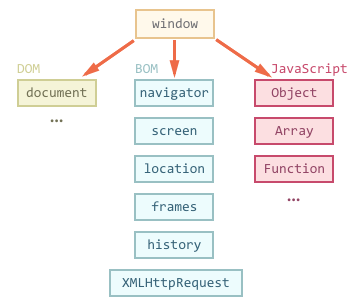 --- # Window Object (cont.) Global variables appear as properties of window object ``` var myName = 'Petro'; console.log(window.myName); //Petro console.log(window['myName']); //Petro window.lastName = 'Jordan'; console.log(lastName) //Jordan window['oneAnotherName'] = 'Ivan'; console.log(oneAnotherName); //Ivan; ``` also ``` window.alert(arg); window.prompt(arg); window.confirm(arg); ``` --- # BOM (Browser object model) The Browser Object Model (BOM) allows JavaScript to "talk to" the browser. - alert/confirm/prompt - delayed execution (setTimeout, setInterval) - Location - Navigator - Data storage (cookies/LocalStorage) - Local/Session storage - Dimensions - ... --- # Delayed Execution Time of code execution can be changed with ["WindowTimers"](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/WindowTimers) `var timer = setTimeout(fn, ms);` execute `fn` after `ms` milliseconds. `typeof timer; // "number"` setTimeout returns an identificator `clearTimeout(timer);` prevents execution of early setted timeout. `var interval = setInterval(fn, ms);` execute `fn` after every `ms` (multiple executions). `clearInterval(interval);` stop interval execution. Execute `fn` after 1/60 (probably) of second. Useful for animations. ``` var animFrame = requestAnimationFrame(fn); cancelAnimationFrame(animFrame); ``` --- ``` function main(){ console.log('A'); setTimeout( function display(){ console.log('B'); } ,0); console.log('C'); } main(); // Output: A -> C -> B ```  --- # Location [Location](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Location) object used to change URL in browser. ``` location.href; // get full URL location.protocol; // get protocol location.host; // get host, w/o url location.pathname; // get pathname, w/o hostname location.port; // get port location.hash; // get hash (#) location.search; // get search (?value=...) // you may set each of this properties, like location.href = 'http://google.com'; // redirect user browser to google.com location.hash = '#11'; // this event fire when hash was changed window.addEventListener('hashchange', function(e) { console.log(e.oldURL + ' -> ' + e.newURL); }); ``` --- # Encoding/decoding Since some characters (like, /, ?, #, :, =, etc) are reserved for using as URL delimiters, as well as non-ascii characters (non-latin alphabet), you need to encode values in order to get correct result. Browsers use escape-sequences, containing '%xx', where xx is a symbol code. Up to 3 '%xx%yy%zz' may be used to encode some wide characters (like japanese symbols). ``` // Encode only non-latin characters, leave all url-specific symbols in place encodeURI(value); // Encode all not-allowed characters, including /, ?, ... encodeURIComponent(value); // Decode only non-latin characters decodeURI(value); // Decode all delimiter characters decodeURIComponent(value); // Base64 String // B for binary (UTF string), A - for ASCII - for Base64 string window.btoa(str); // encode window.atob(str); // decode ``` [Article Explaining URL and encodings](http://www.skorks.com/2010/05/what-every-developer-should-know-about-urls/) --- # Navigator [Navigator](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Navigator) object is used to detect client browser type. Since earlier many sites support only Netscape - all browsers should use _'Netscape'_ as values for `appName`. This, actually, is written in standard, so this property is not very useful. ``` // get user-agent string, which can be parsed and detect browser. navigator.userAgent; // Array of installed plugins. May be used to detect installed plugins, like Adobe Flash navigator.plugins; // Current system language navigator.language; // If user allows you to track his position you may use geolocation to retrieve // user current coordinates (HTML5) navigator.geolocation.getCurrentPosition(success, error); var positionChangeWatch = navigator.geolocation.watchPosition(success, error); navigator.geolocation.clearWatch(positionChangeWatch); ``` --- # Local/Session storage Data is stored as simple key-value pairs, both strings. [localStorage](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Window/localStorage) saves values forever, while [sessionStorage](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Window/sessionStorage) - only until browser closed. `localStorage.setItem(key, value);` store value in storage `localStorage.getItem(key);` get value from storage. If value does not exist `null` is returned. `localStorage.removeItem(key);` remove key-value pair from storage. `localStorage.clear();` remove all values from storage. Same methods available for `sessionStorage`. --- # Dimensions `window.innerWidth` get page working area width. `window.innerHeight` get page working area height. `screen` [Screen](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Screen) object with dimensions, orientation, pixelDepth, etc. --- # RegExp A regular expression is an object that describes a pattern of characters. Regular expressions are used to perform pattern-matching and "search-and-replace" functions on text. `/word/` pattern that matches "word", using regex syntax `var regexp = new RegExp('word', '');` pattern that matches "word" using RegExp object `.` matches _any_ character (except newline) `/o.o/` matches 'oao', 'obo', 'o o', 'o-o' ... `^` indicates beginning of line `$` indicates end of line `/^word$/` matches lines that consist only of 'word'. RegExps are matched __line by line__. https://regex101.com/ http://regexr.com/ http://regexper.com/ --- # RegExp Usage Methods: __RegExp__.test(string); tests "string" to match regexp. `/world/.test('hello, world!'); // -> true` __String__.match(regexp); matches string, returning null if no matches found, array of matches otherwise. `'hello, world'.match(/world/); // -> ["world"]` Also regexp may be used in ''.replace: ``` 'testtest'.replace(/test/, function(match) { return match + '.'; }); // test.test ``` --- # RegExp Grouping Groups: `[]` - Character set, match any of given characters `[a-z]` - Any of lowercase letters. `(...)` - create "match group". Groups are accessible as $1..$9 ``` 'hello world'.replace(/(\w+)/g, '-$1-'); // "-hello- -world-" ``` --- # RegExp Repeating `{count}` - previous symbol repeated exactly 'count' times Example: `/a{2}/` - matches 'aa' `{x, y}` - previous symbol (or group) repeated from "x" to "y" times Example: `/a{1, 3}/` - matches 'a' or 'aa' or 'aaa' Special symbols: `*` previous symbol repeated from 0 to infinite times. Equivalent `{0,}` `?` previous symbol repeated 0 or 1 times. Equivalent `{0,1}` `+` previous symbol repeated 1 to infinite times. Equivalent `{1,}` --- # RegExp Modifiers `g` - global search, match all occurences. `i` - ignore case, match letters ignoring case. `m` - multiline, match all lines, not line by line. --- # RegExp Symbol Classes `\d` - digits `\D` - non-digits `\w` - word symbols [a-zA-Z0-9_] `\W` - non-word symbols `\s` - white-space symbols `\S` - non white-space symbols If you need to use some of reserved symbol as match you need to quote them with "`\`": Reserved symbols: `(, ), \, /, *, +, ?, ., [, ]` --- # Further reading BOM: - https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/WindowTimers - https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Location - https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Navigator - https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Window/localStorage RegExp: - [Learning Regex The Hard Way](http://regex.learncodethehardway.org/book/) - [The Bastards Book Of Regular Expressions](https://leanpub.com/bastards-regexes) - [RegExp Playground](http://regexr.com/)